In today’s digitally driven world, e-commerce has revolutionized the way businesses operate and consumers shop. Understanding the intricacies of e-commerce is crucial for both businesses seeking to expand their reach and individuals looking to navigate the online marketplace effectively. This article, “Demystifying E-Commerce: A Clear Explanation of How It Works and Its Benefits,” aims to provide a comprehensive overview of e-commerce, breaking down its core components and exploring the numerous advantages it offers.
From the fundamental mechanisms of online transactions to the broader impact on the global economy, we will delve into the essential aspects of e-commerce. We will explore the various e-commerce models, including business-to-consumer (B2C), business-to-business (B2B), and consumer-to-consumer (C2C), highlighting their unique characteristics and functionalities. Furthermore, we will examine the key benefits of e-commerce, such as increased convenience, wider product selection, and competitive pricing, for both businesses and consumers. Join us as we demystify the world of e-commerce and uncover its transformative power.
Defining E-Commerce and Its Various Forms
E-commerce, short for electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods or services using the internet. It encompasses a wide range of activities, from online shopping to electronic funds transfers and online auctions.
E-commerce can take various forms, each characterized by the parties involved in the transaction. Some common types include:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): This is the most common form, where businesses sell products or services directly to individual consumers. Think online retail stores.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): Here, businesses transact with each other, such as a wholesaler selling to a retailer.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): This involves transactions between individuals, often facilitated by platforms like online marketplaces or auction sites.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B): In this model, individuals offer services or products to businesses, such as freelance work or customer reviews.
- Government-to-Citizen (G2C): This pertains to online government services provided to citizens, like paying taxes or renewing licenses.
The Key Components of a Successful E-Commerce Operation
A thriving e-commerce business relies on several key components working together seamlessly. A robust website is paramount, offering intuitive navigation, detailed product information, and secure checkout processes. This digital storefront is the core of your online presence.
Efficient order fulfillment is crucial. This encompasses inventory management, timely processing, and reliable shipping. Customers expect quick and accurate delivery, making a streamlined fulfillment process essential.
Customer service plays a vital role in building trust and loyalty. Promptly addressing inquiries, resolving issues, and providing helpful support cultivates positive customer relationships. This includes clear return policies and easy communication channels.
Marketing and promotion are essential for driving traffic and generating sales. Targeted advertising, social media engagement, and search engine optimization are key strategies for reaching potential customers and building brand awareness.
Finally, robust security measures are non-negotiable. Protecting customer data and ensuring secure transactions builds trust and safeguards your business reputation. This includes secure payment gateways and data encryption.
Understanding the E-Commerce Sales Process

The e-commerce sales process, while varying slightly between businesses, generally follows a predictable pattern. It begins with the discovery phase where potential customers find products through browsing, searching, or marketing campaigns.
Next is the consideration phase. Here, shoppers evaluate product details, compare prices, and read reviews. A clear and informative product page is crucial at this stage.
The decision phase involves adding the chosen product to the cart. A streamlined checkout process is essential to minimize cart abandonment.
Payment is the next step. Offering various secure payment options enhances the customer experience and builds trust.
After successful payment, the fulfillment process begins. This involves order processing, packaging, and shipping. Transparent shipping information and timely delivery are critical.
Finally, the post-purchase experience plays a vital role in customer retention. Follow-up emails, support services, and opportunities for feedback contribute to overall satisfaction and encourage repeat purchases.
Exploring Different E-Commerce Business Models
E-commerce encompasses a variety of business models, each with its own approach to online sales. Understanding these models is crucial for choosing the right strategy for your business.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
This is the most common model, where businesses sell products or services directly to individual consumers. Think of online retailers like clothing stores or electronics vendors.
Business-to-Business (B2B)
In B2B e-commerce, transactions occur between businesses. This often involves wholesale distributors, software providers, or manufacturers selling to other businesses.
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
C2C platforms facilitate transactions between individual consumers. Online marketplaces like auction sites or classified ad websites are prime examples of this model.
Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
This model reverses the traditional flow, with consumers offering products or services to businesses. Examples include freelance platforms where individuals offer their skills to companies.
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C)
D2C involves businesses selling their products directly to consumers, bypassing traditional retail channels. This allows for greater control over branding and customer relationships.
Building an Effective E-Commerce Marketing Strategy
A robust marketing strategy is crucial for e-commerce success. It involves understanding your target audience and tailoring your efforts to reach them effectively. This requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing various digital channels.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is essential for organic visibility. Optimizing your website and product listings for relevant keywords helps improve search engine rankings, driving organic traffic to your store.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising, particularly through platforms like Google Ads, allows you to target specific demographics and keywords. This provides a direct route to reach potential customers actively searching for products like yours.
Social Media Marketing leverages the power of platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Pinterest to connect with your audience. Engaging content and targeted advertising can build brand awareness and drive traffic.
Email marketing remains a powerful tool for nurturing leads and retaining customers. Personalized email campaigns can promote new products, offer exclusive deals, and build customer loyalty.
Choosing the Right E-Commerce Platform for Your Business
Selecting the right e-commerce platform is a critical decision that can significantly impact your online business’s success. Various factors influence this choice, including your business size, budget, technical expertise, and future scalability needs.
Key considerations when evaluating platforms include features, pricing, ease of use, and available support. Some platforms cater to small businesses with basic online stores, while others offer robust enterprise-level solutions with advanced functionalities like inventory management and customer relationship management (CRM) integrations.
Popular e-commerce platforms offer different pricing models, ranging from subscription-based services to open-source options. Thoroughly researching each platform’s features, limitations, and pricing structure is essential for making an informed decision.
Consider your technical capabilities. Some platforms require coding knowledge for customization, while others provide user-friendly interfaces for managing your online store without technical expertise.
The Importance of Security and Compliance in E-Commerce
Security and compliance are paramount in e-commerce. Protecting customer data and adhering to regulations builds trust and safeguards your business.
Data breaches can have devastating consequences, including financial loss, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Implementing robust security measures is crucial.
PCI DSS compliance is essential for businesses that process credit card payments. This standard ensures the secure handling of sensitive cardholder information.
Other vital security measures include SSL certificates for encrypting data, strong passwords, and regular security audits. Staying informed about evolving threats and best practices is crucial for maintaining a secure e-commerce environment.
Compliance extends beyond payment security. Depending on your industry and location, you might need to comply with regulations like GDPR or CCPA, governing data privacy and user rights.
Analyzing E-Commerce Data to Improve Performance
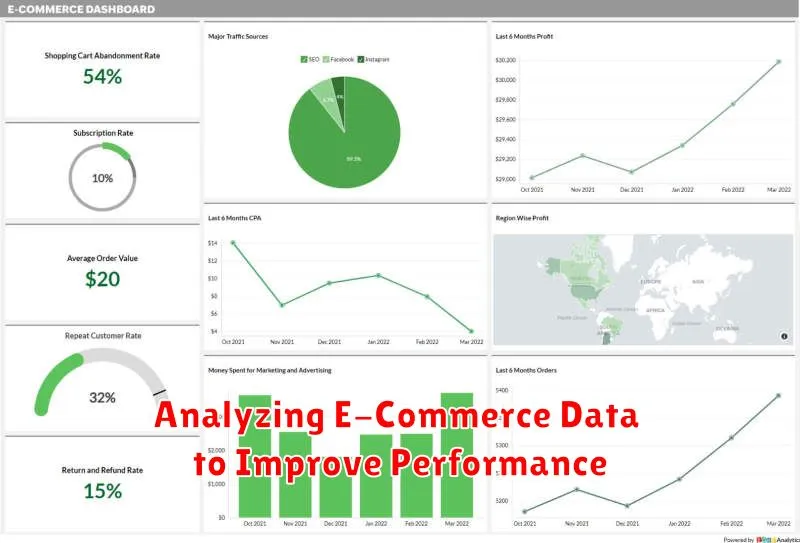
Data analysis is crucial for optimizing e-commerce performance. By examining key metrics, businesses can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provide valuable insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and marketing effectiveness. Tracking KPIs like conversion rates, average order value (AOV), and customer lifetime value (CLTV) allows businesses to understand what’s working and what needs adjustment.
Website analytics tools offer data on website traffic, bounce rates, and popular product pages. This information can be used to optimize website design, improve navigation, and personalize the customer experience.
Sales data reveals which products are selling well and which are underperforming. Analyzing sales data by product category, region, and time period can inform inventory management decisions and marketing campaigns.
By leveraging these data sources, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their customers and operations, ultimately leading to improved performance and profitability.

